How to Convert Fahrenheit (F) & Celsius (C)?
With this temperature converter tool you can Convert Fahrenheit (F) to Celsius (C) and Celsius (C) to Fahrenheit (F).
How to Convert C to F
- To convert C to F press °C→°F button
- Enter temperature in Celsius (C)
- And press convert.
How to Convert F to C
- To convert F to C press °F→°C button
- Enter temperature in Fahrenheit (F)
- And press convert.
Keep reading if you would like to find out:
- What the Fahrenheit (F) to Celsius (C) Conversion formula is, and how it can be used;
- What the Celsius (C) to Fahrenheit (F) Conversion formula is, and how it can be used;
- How to convert temperature between Fahrenheit (F) and Celsius (C) manually?
- To know more about medical relevence of temperature
- These values represent normal body temperature on different sites.
- Main Temperature Assessment Sites of our body
-
Commonly Asked C to F and F to C Conversions:
-
Other calculators you should check out if you are interested in this topic.
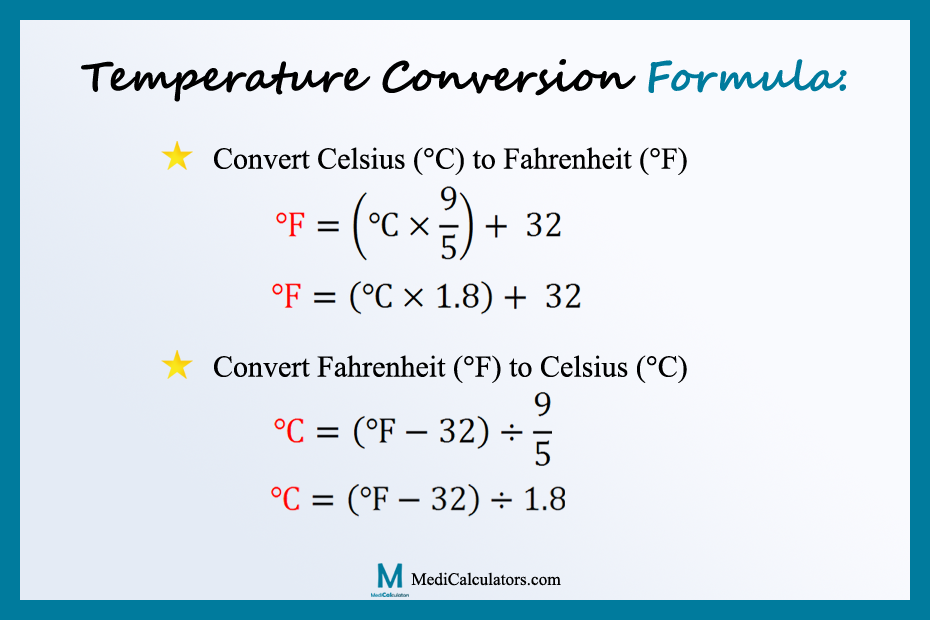
Temperature Conversion Formulas:
Celsius to Fahrenheit (C to F) Conversion Formula
This formula is used to convert Celsius (C) to Fahrenheit (F) is:
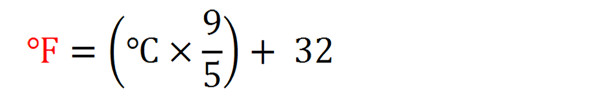
Example
1. How to Convert 37 Celsius to Fahrenheit.
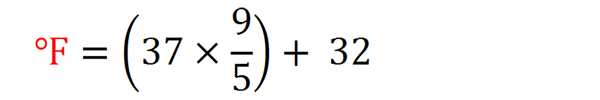
The answer is 98.6 F.
Fahrenheit to Celsius (F to C) Conversion Formula
This formula is used to Convert Fahrenheit (F) to Celsius (centigrade) (C) is:
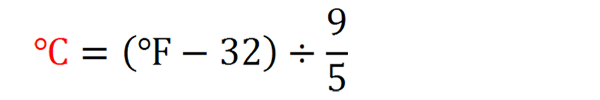
Example
How to Convert 98.6 Fahrenheit to Celsius.
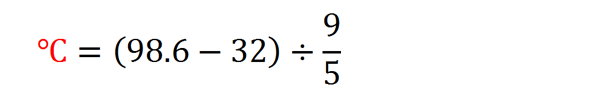
The answer is 37 C
Medical Relevance of Temperature
Core temperature
The temperature of the deep tissues of the body—the “core” of the body—remains almost exactly constant, within ±1°F (±0.6°C), day in and day out except when a person febrile illness.
Normal core temperature
The average normal core temperature is generally considered to be between 98.0° and 98.6°F when measured orally and about 1°F higher when measured rectally.
Hyperpyrexia
Occurs between 105—108°F. Circulatory shock, cell destruction and organ failure are followed by death.
Hypothermia
Occurs between 94—77°F. Once the core temperature falls below 85°F temperature regulation is lost. Death by cardiac arrest or ventricular fibrillation occurs once body temperature falls to 77°F.
Temperature Assessment Sites
Various sites such as Pulmonary artery (most accurate), Esophageal, Bladder, Rectal, Tympanic, Oral, Axillary and Forehead (least accurate)
| Assessment Sites | Temperature in Celsius (C°) & Fahrenheit (F°) |
| Oral | 37 Celsius which is equal to 98.6 Fahrenheit |
| Rectal | 37.5 Celsius which is equal to 99.5 Fahrenheit |
| Tympanic (Ear) | 36.8 Celsius which is equal to 98.2 Fahrenheit |
| Axillary (Armpit) | 36.4 Celsius which is equal to 97.6 Fahrenheit |
FAQs
The formula to convert Celsius (C) to Fahrenheit (F) is: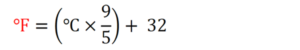
The formula to convert Fahrenheit (F) to Celsius (C) is: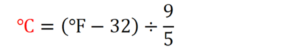
Different countries use different temperature scales. Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is necessary for interpreting weather forecasts, medical readings, cooking recipes, and scientific data across different regions.
Yes, other temperature scales include Kelvin (K), which is used in scientific contexts, especially in thermodynamics, and Rankine (°R), which is used in some engineering fields.
Commonly Asked Celsius to Fahrenheit (C to F) Conversions:
200 celsius to fahrenheit
- 200 C to F = 392 Fahrenheit
190 celsius to fahrenheit
- 190 C to F = 374 Fahrenheit
180 celsius to fahrenheit
- 180 C to F = 356 Fahrenheit
150 celsius to fahrenheit
- 150 C to F = 302 Fahrenheit
121 celsius to fahrenheit (121 celsius is Autoclave Temperature)
- 121 C to F = 249.8 Fahrenheit
100 celsius to fahrenheit (Boiling point of water)
- 100 C to F = 212 Fahrenheit
70 celsius to fahrenheit
- 70 C to F = 158 Fahrenheit
50 celsius to fahrenheit
- 50 C to F = 122 Fahrenheit
48 celsius to fahrenheit
- 48 C to F = 118.4 Fahrenheit
45 celsius to fahrenheit
- 45 C to F = 113 Fahrenheit
42 celsius to fahrenheit
- 42 C to F = 107.6 Fahrenheit
40 celsius to fahrenheit
- 40 C to F = 104 Fahrenheit
39 celsius to fahrenheit
- 39 C to F = 102.2 Fahrenheit
38 celsius to fahrenheit
- 38 C to F = 100.4 Fahrenheit
37 celsius to fahrenheit
- 37 C to F = 98.6 Fahrenheit
36 celsius to fahrenheit
- 36 C to F = 96.8 Fahrenheit
32 celsius to fahrenheit
- 30 C to F = 89.6 Fahrenheit
30 celsius to fahrenheit
- 30 C to F = 86 Fahrenheit
25 celsius to fahrenheit
- 25 C to F = 77 Fahrenheit
15 celsius to fahrenheit
- 15 C to F = 59 Fahrenheit
0 celsius to fahrenheit (Water freezing Point)
- 0 C to F = 32 Fahrenheit
-10 celsius to fahrenheit
- -10 C to F = 14 Fahrenheit
-40 celsius to fahrenheit
- -40 C to F = -40 Fahrenheit
Commonly asked fahrenheit to celsius (F to C) conversions:
350 fahrenheit to celsius
- 350 F to C = 176.7 celsius
212 fahrenheit to celsius
- 212 F to C = 100 celsius
105 fahrenheit to celsius
- 105 F to C = 40.2 celsius
105 fahrenheit to celsius
- 105 F to C = 40.2 celsius
102 fahrenheit to celsius
- 102 F to C = 38.9 celsius
101 fahrenheit to celsius
- 101 F to C = 38.3 celsius
100 fahrenheit to celsius
- 100 F to C = 37.8 celsius
99 fahrenheit to celsius
- 99 F to C = 37.2 celsius
98 fahrenheit to celsius
- 98 F to C = 36.7 celsius
97 fahrenheit to celsius
- 97 F to C = 36.1 celsius
96 fahrenheit to celsius
- 96 F to C = 35.6 celsius
80 fahrenheit to celsius
- 80 F to C = 26.7 celsius
75 fahrenheit to celsius
- 75 F to C = 23.9 celsius
72 fahrenheit to celsius
- 72 F to C = 22.2 celsius
68 fahrenheit to celsius
- 68 F to C = 20 celsius
50 fahrenheit to celsius
- 50 F to C = 10 celsius
Also Check:
References
- Lillis, C., LeMone, P., LeBon, M., & Lynn, P. (2010). Fundamentals of nursing: The art and science of nursing care. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Hall, J. E., & Hall, M. E. (2020). Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology e-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
- Dante, A., Franconi, I., Marucci, A. R., Alfes, C. M., & Lancia, L. (2020). Evaluating the interchangeability of forehead, tympanic, and axillary thermometers in Italian paediatric clinical settings: Results of a multicentre observational study. Journal of pediatric nursing, 52, e21-e25.
- Geneva, I. I., Cuzzo, B., Fazili, T., & Javaid, W. (2019, April). Normal body temperature: a systematic review. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases (Vol. 6, No. 4, p. ofz032). US: Oxford University Press.
- Ng, D. K. K., Chan, C. H., Chan, E. Y. T., Kwok, K. L., Chow, P. Y., Lau, W. F., & Ho, J. C. S. (2005). A brief report on the normal range of forehead temperature as determined by noncontact, handheld, infrared thermometer. American journal of infection control, 33(4), 227-229.
- Coran, A. G., Caldamone, A., Adzick, N. S., Krummel, T. M., Laberge, J. M., & Shamberger, R. (2012). Pediatric surgery E-book (Vol. 2). Elsevier Health Sciences.
- Robinson, J. L., Seal, R. F., Spady, D. W., & Joffres, M. R. (1998). Comparison of esophageal, rectal, axillary, bladder, tympanic, and pulmonary artery temperatures in children. The Journal of pediatrics, 133(4), 553-556.
Pingback: Dosage Calculation Conversions - Medicalculators
To the medicalculators.com owner, Thanks for the educational content!