Welcome back to our med calculation series. The first two installments we reviewed two common calculation methods – the universal formula and dimensional analysis (DA). In Part 3, we used Dimensional Analysis to calculate continuous intravenous (IV) drips, beginning with units per hour (unit/hr to ml/hr). In this blog, we will now use the Dimentional Analysis method to calculate continuous IV drips in micrograms per minute (mcg/min to ml/hr and ml/hr to mcg/min).
After reading this blog you are able to calculate:
- mcg/min to ml/hr
- unit/min to ml/hr
- mg/min to ml/hr
- ml/hr to mcg/min
- ml/hr to unit/min
- ml/hr to mg/min
Intravenous Drips: Convert mcg/min to mL/hr
Example: The provider places an order for a nitroglycerin drip at 10 mcg/minute.The pharmacy delivers the infusion bag of nitroglycerin and the label on the bottle reads 50 mg in 500 mL 0.9% sodium chloride solution. At what rate should you set the IV pump?
Step 1: What label is needed? You want to set the IV pump in mL/hr. This is placed on the left side of the equation.

Steps 2: Next we need to convert the concentration from mg/mL to mcg/mL. There are 50 mg in 500 mL. Convert the mg to mcg by multiplying by 1000.

The concentration is 100 mcg/mL.
Step 3: Place the same label in numerator on the right side of the equation. Flip the concentration so that mL is in the numerator and 100 mcg is in the denominator. Then alternate labels in the numerator and denominator so the labels cancel out.
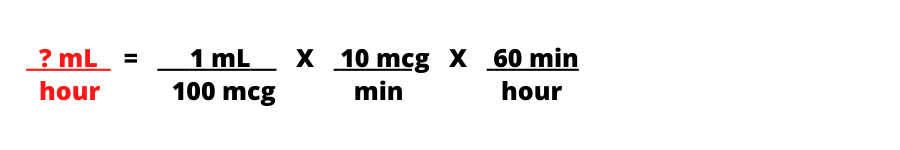
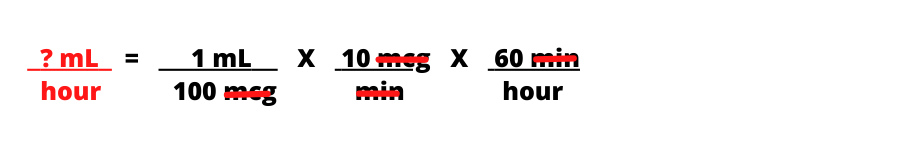
Step 4: Multiply numerators, multiply denominators, then divide numerator by denominator.

Answer: 6 mL/hour
Intravenous Drips: Convert mL/hour to mcg/min
Now let’s reverse the problem and convert mL/hr to find the pump rate mcg/min.
Example: You receive shift report that your patient is on a nitroglycerin drip for blood pressure control. You check the pump and it is running at 6 mL/hour. The label on the bottle reads 50 mg in 500 mL 0.9% sodium chloride solution. How many mcg/min is the patient receiving?
Step 1: What label is needed? Nitroglycerin is delivered in a continuous drip dosed at mcg/min. This is placed on the left side of the equation.

Step 2: Next we need to convert the concentration from mg/mL to mcg/mL in order to get the same label in the numerator. There are 50 mg in 500 mL. Convert the mg to mcg by multiplying by 1000.

The concentration is 100 mcg/mL.
Step 3: Place the same label in numerator on the right side of the equation then alternate labels in the numerator and denominator so the labels cancel out.
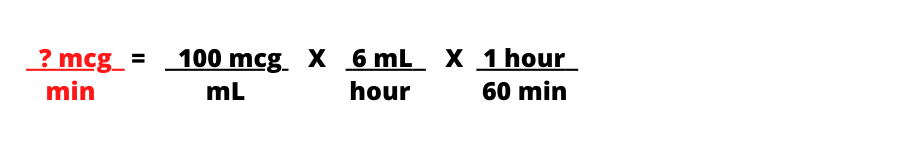 Step 4: Multiply numerators, multiply denominators, then divide numerator by denominator.
Step 4: Multiply numerators, multiply denominators, then divide numerator by denominator.
Answer: 10 mcg/min
Click Here for Continuous IV Drips Calculator which allows you to calculate:
- mcg/min to ml/hr Calculator
- units/min to ml/hr Calculator
- mg/min to ml/hr Calculator
- mcg/hr to ml/hr calculator
- units/hr to ml/hr calculator
- mg/hr to ml/hr calculator
Remember These Tips:
- Check that your answer makes sense clinically.
- Double check your work.
- Have a colleague or pharmacist check your work.
- Know general therapeutic drug doses for commonly administered medications
I hope this review has been helpful. Next, we will review continuous IV infusions for weight-based drugs (mcg/kg/min) using dimensional analysis. Be sure to check back then!